The Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development has released the online database OECD Health Statistics 2019 on July 2.
The database offers the most comprehensive source of comparable statistics on health and health systems across OECD countries. It is an essential tool to carry out comparative analyses and draw lessons from international comparisons of diverse health systems.
Amongst the datasets are tax and transfer-related indicators such as health expenditure and financing, as well as social protection.
Key figures
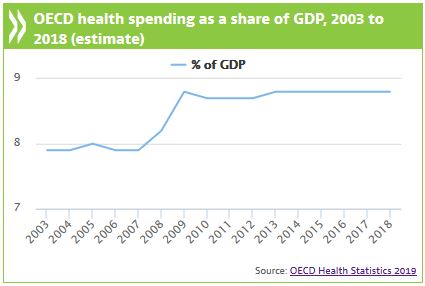
- Since 2009, average health spending as a share of GDP has remained relatively stable across the OECD at around 8.8 percent, as growth in health spending has remained in line with overall economic growth since the economic crisis.
- At 17.1 percent, the United States spent the highest share of GDP on health in 2017, while Turkey allocated around 4.2 percent.
- In 2017, Australia’s expenditure on health represented 9.2 percent of its GDP. Australians’ out-of-pocket expenditure was 18.3 percent of current expenditure on health for 2016 (the latest year available), below the OECD average of 20.6 percent.
(Source: OECD).
From the blog:
Socio-Economic Disparities in American Healthcare Spending: The Role of Public vs Private Insurance, by Elena Capatina, Michael Keane and Shiko Maruyama.
Introducing a GP Copayment in Australia: Who Would Carry the Cost Burden?, by Rosemary Elkins and Stefanie Schurer.



Recent Comments